|
Diagnostic and Lab Services
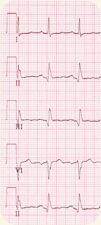 Electrocardiogram (EKG)
An electrocardiogram (abbreviated as EKG or ECG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or "wave") travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on an EKG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers. There's no pain or risk associated with having an electrocardiogram.
An EKG gives two major kinds of information. First, by measuring time intervals on the EKG, a doctor can determine how long the electrical wave takes to pass through the heart. Finding out how long a wave takes to travel from one part of the heart to the next shows if the electrical activity is normal or slow, fast or irregular. Second, by measuring the amount of electrical activity passing through the heart muscle, a cardiologist may be able to find out if parts of the heart are too large or are overworked. This test is done to check the heart's electrical activity, find the cause of unexplained chest pain or symptoms of heart disease, find out if the heart chamber walls are too thick (hypertrophied heart muscle), and generally check the health of the heart.  Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to produce a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen. It can evaluate the abdominal aorta, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys. Ultrasound imaging is a completely safe, noninvasive, and painless procedure which helps doctors diagnose and treat medical conditions such as kidney stones, tumors, and other urinary bladder disorders.
A pelvic ultrasound evaluates the structures and organs in the lower abdominal area (pelvis). The types of pelvic ultrasound are abdominal, vaginal for women, and rectal for men. Ultrasound exams can help diagnose symptoms experienced by women such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, and other menstrual problems. It can also help identify palpable masses such as ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids, as well as ovarian cancer or uterine cancer. In men, a pelvic or abdominal ultrasound is used to evaluate the bladder, seminal vesicles, and prostate. A thyroid ultrasound assesses the health of the thyroid, a metabolism-regulating gland located in front of the neck just below the Adam's apple. This is usually done to evaluate abnormal thyroid function or a growth on the thyroid gland. The thryoid ultrasound can help distinguish a benign lump from abnormal tissue that may be cancerous (a malignant tumor).  Bone Density Test
A bone density test assesses whether you have or are at risk for developing osteoporosis, a disease that causes bones to become more fragile and likely to break. This test uses X-rays to measure how many grams of calcium and other bone minerals are in a segment of bone, and is a fairly accurate predictor of your risk of fracture. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends bone density testing for women age 65 or older, postmenopausal woman under age 65 with risk factors for osteoporosis, men age 70 or older, and men from 50–70 with risk factors for osteoporosis.
Bone density tests are usually done on bones that are most likely to break because of osteoporosis, including the lower spine bones, the narrow neck of your thigh bone (femur) where it adjoins your hip, and bones in your wrist and forearm. The test is quick and painless, and our office utilizes efficient technology to enhance dose efficiency and achieve excellent precision throughout the spine, femur, and total body measurements. 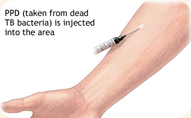 Tuberculin Test
Also known as the tuberculosis skin test or PPD test, the tuberculin test is used to determine if someone has developed an immune response to the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB). The test is done by injecting a small amount of TB antigens (called purified protein derivative, or PPD) under the top layer of skin on the forearm. If you have ever been exposed to the TB bacteria, your skin will react to the antigens by developing a firm red bump at the site within 2 days. "Reading" the skin test means detecting and measuring the diameter of a raised, thickened local area of skin reaction, referred to as the induration. This response can occur if you currently have TB, if you have previously been exposed to TB, or if you received the BCG vaccine against TB outside of the U.S.
 Laboratory Testing
Laboratory tests check a sample of your blood, urine, feces, or body fluids/tissues. The test samples are then analyzed to see if your results fall within the normal range. Many factors affect test results, including sex, age, race, diet, and medicines. They also help doctors diagnose medical conditions, plan or evaluate treatments, and monitor diseases.
Laboratory tests are often part of a routine checkup to look for changes in your health. Our office performs routine labs as part of each annual physical exam, which include a complete blood count; liver, kidney, and thyroid function assessments; a lipid panel that includes measures of cholesterol and triglycerides; a glucose blood test; urinalysis; a stool guaiac test that detects hidden blood in the stool; a prostate test for men over 50; and a pap smear for women. We also offer cardiovascular lab testing, diabetes screening, STD screening, and HIV screening. | |||